Short Summary
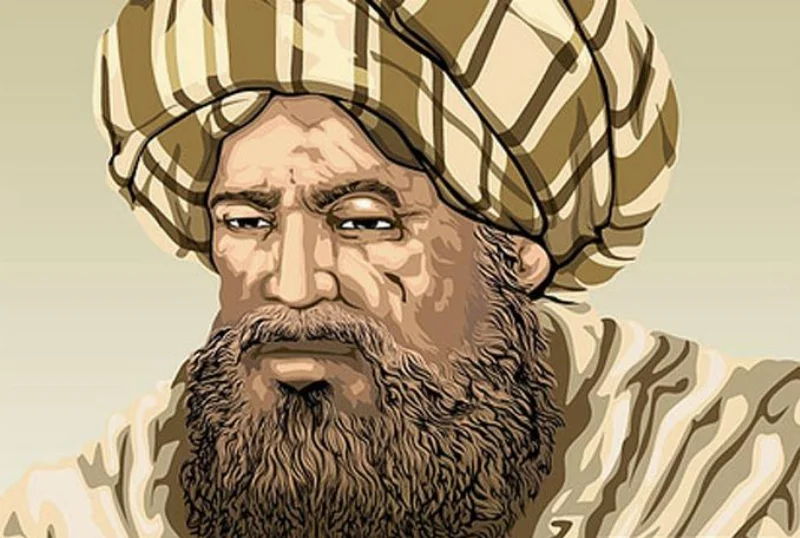
Al-Battani was a renowned Arab astronomer and mathematician born in the 9th century. Known for his influential work in astronomy, his precise calculations of the solar year and lunar month significantly impacted the field. His treatise, the "Book of Astronomical Tables," was highly regarded and used by later scholars in Europe. Al-Battani's contributions laid foundational insights that furthered the understanding of celestial movements, making him a pivotal figure in both Islamic Golden Age science and Western astronomy.
Early Life & Education
Al-Battani was born around 858 CE in Harran, in the region that is now part of modern-day Turkey. He descended from a lineage of scholars, which greatly influenced his pursuit of knowledge. His father, Jabir Ibn Sin'an al-Harrani, was also a well-known scientist, providing a stimulating intellectual environment. Al-Battani received early education in his hometown before moving to Raqqa, where he studied under prominent scholars of the time. His education was deeply rooted in the Islamic scientific tradition, with a strong emphasis on mathematics and astronomy.
Career Highlights
Throughout his career, Al-Battani made significant contributions to the fields of astronomy and mathematics. One of his most notable works was the "Kitab al-Zij," also known as the "Book of Astronomical Tables," which compiled his astronomical observations and calculations. His career was marked by precise measurements of celestial bodies, including the length of the solar year, which he calculated with remarkable accuracy. Al-Battani's work laid the groundwork for future astronomers, influencing the development of trigonometry and the use of sine functions. His observations and theories were later translated into Latin, spreading his influence throughout Europe.
Major Achievements
- Calculated the solar year as 365 days, 5 hours, 46 minutes, and 24 seconds, which was remarkably precise for his time.
- Produced a comprehensive set of astronomical tables that were used for centuries by scholars in both the Islamic world and Europe.
- Developed trigonometric relationships and introduced the use of sine functions, significantly advancing mathematical practices.
- Improved the understanding of the motion of the sun and moon, contributing to more accurate astronomical predictions.
Famous Quotes
- "The science of astronomy is a noble one, for it elevates the human spirit to contemplate the universe."
- "Through understanding the heavens, we comprehend the divine order."
Interesting Facts
- Al-Battani's work was used by Copernicus in developing his heliocentric model of the solar system.
- He was also known as Albatenius in the Latin translations of his works.
- Al-Battani conducted his observations without the use of telescopes, relying solely on astrolabes and quadrants.
- His astronomical tables were used in the West until the Renaissance era.
- He corrected some of Ptolemy's astronomical calculations, showing his advanced understanding of the field.
Legacy / Influence
Al-Battani's work had a lasting impact on both Islamic and Western astronomy. His precise calculations and development of trigonometric functions were pivotal in advancing the study of celestial bodies. His influence reached far beyond his time, with his works being referenced by Renaissance astronomers, thus bridging the gap between ancient and modern astronomical studies.
FAQ
Q: Why is Al-Battani famous?
A: Because of his significant contributions to astronomy and mathematics, including precise calculations of the solar year and development of trigonometric functions.
Q: What was Al-Battani's most famous work?
A: His most famous work was the "Book of Astronomical Tables," which was influential in both the Islamic world and Europe.
Q: How did Al-Battani influence later astronomers?
A: His works were referenced by later astronomers such as Copernicus, aiding in the development of the heliocentric model of the solar system.