Short Summary
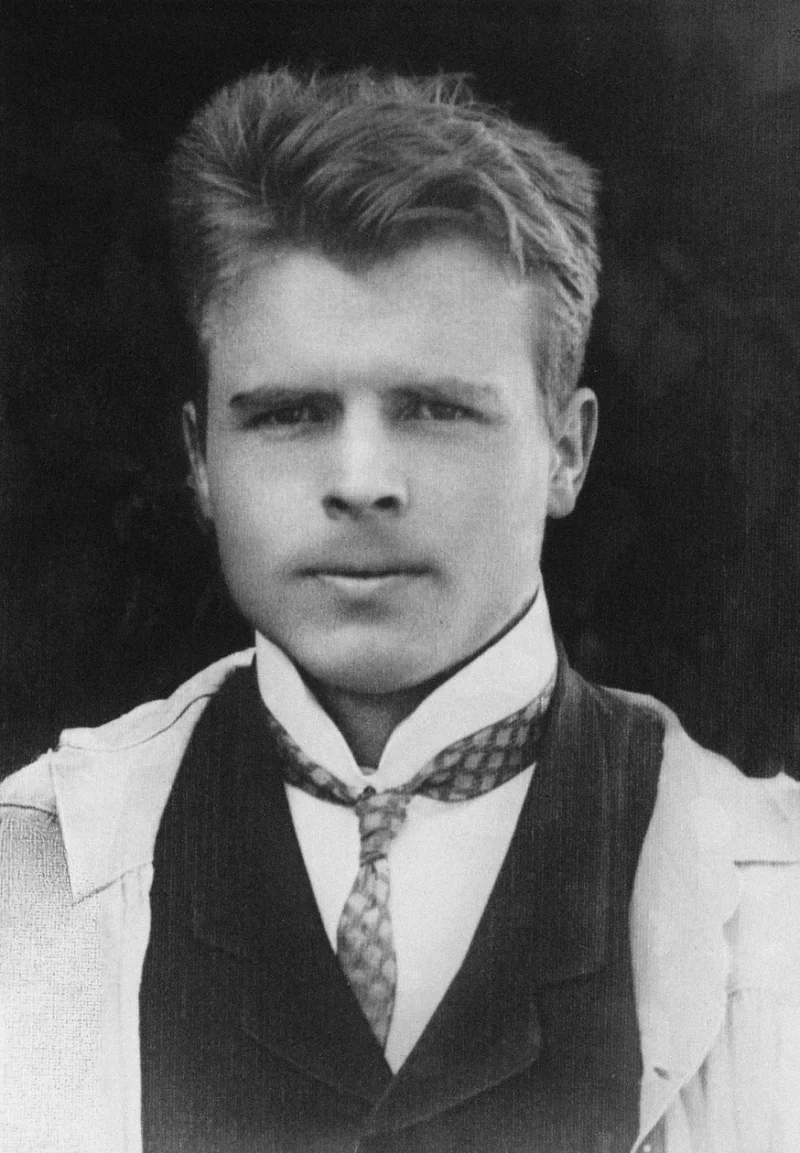
Alfred Kinsey was an American biologist and sexologist renowned for his pioneering research on human sexuality. He gained prominence through the publication of the "Kinsey Reports," which were groundbreaking studies on sexual behavior in the human male and female. His work challenged conventional norms and ignited widespread discussion about sexual practices and attitudes in the United States, laying the groundwork for modern sexology.
Early Life & Education
Born on June 23, 1894, in Hoboken, New Jersey, Alfred Kinsey grew up in a strict Methodist household. His father, Alfred Seguine Kinsey, was a professor of engineering, which instilled in him a respect for rigorous academic pursuits. Kinsey's early fascination with nature led him to pursue a career in biology. He attended Bowdoin College, where he excelled in zoology, and later earned his doctorate from Harvard University in 1920. His academic journey was marked by a deep interest in entomology, particularly the study of gall wasps, which laid the foundation for his methodical research skills.
Career Highlights
After completing his education, Kinsey joined the faculty at Indiana University in 1920, where he initially focused on the study of insects. However, his career took a defining turn in the late 1930s when he began collecting sexual histories from his students. This informal study led to the formation of the Institute for Sex Research in 1947. Kinsey's meticulous data collection and analysis resulted in the publication of "Sexual Behavior in the Human Male" in 1948, followed by "Sexual Behavior in the Human Female" in 1953. These landmark studies were instrumental in the academic and public discourse on human sexuality.
Major Achievements
- Publication of "Sexual Behavior in the Human Male" in 1948, a groundbreaking study on male sexuality.
- Publication of "Sexual Behavior in the Human Female" in 1953, which expanded knowledge on female sexuality.
- Founded the Institute for Sex Research at Indiana University in 1947, which became a leading center for sexology research.
- Pioneered the use of large-scale interviews for collecting data on human sexual behavior.
Famous Quotes
- "The only unnatural sex act is that which you cannot perform."
- "We are the recorders and reporters of facts—not the judges of the behaviors we describe."
Interesting Facts
- Kinsey's research was funded in part by the Rockefeller Foundation, which faced pressure from conservative groups to end its support.
- He collected over 18,000 sexual histories for his studies, using a detailed interview technique.
- His work is often credited with contributing to the sexual revolution of the 1960s.
- Kinsey's methodology and findings were controversial and faced criticism from various social and religious groups.
- He was an avid collector of gall wasps, amassing millions of specimens during his career.
Legacy / Influence
Kinsey's research had a profound influence on the study of human sexuality, challenging societal norms and encouraging open discussions about sexual behavior. His work laid the foundation for modern sexology and inspired subsequent generations of researchers to explore human sexuality more openly and scientifically. Despite controversies, his contributions remain a cornerstone in the field, fostering a greater understanding of sexual diversity and practices.
FAQ
Q: Why is Alfred Kinsey famous?
A: He is famous for his groundbreaking research on human sexuality, particularly the "Kinsey Reports."
Q: What were the "Kinsey Reports"?
A: They were comprehensive studies on sexual behavior published as "Sexual Behavior in the Human Male" and "Sexual Behavior in the Human Female."
Q: What institution did he establish?
A: He established the Institute for Sex Research at Indiana University in 1947.