Short Summary
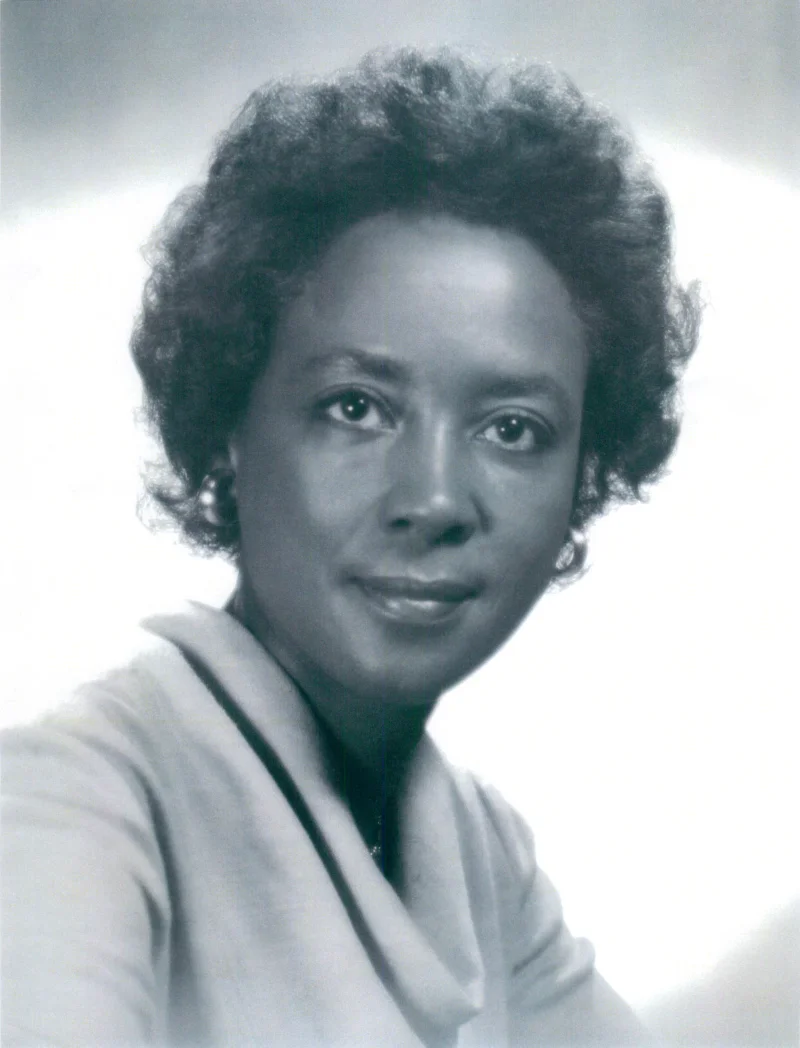
Annie Easley was an influential American computer scientist, mathematician, and rocket scientist who made significant contributions to the fields of technology and space exploration. She is renowned for her work at NASA, where she developed software for the Centaur rocket and contributed to alternative energy projects. Easley’s pioneering efforts helped pave the way for women and African Americans in STEM fields, and her legacy continues to inspire future generations of scientists and engineers.
Early Life & Education
Annie Jean Easley was born on April 23, 1933, in Birmingham, Alabama. Raised by her mother, she grew up in an environment that emphasized the importance of education and perseverance. Easley attended and graduated from Holy Family High School in Birmingham, where she excelled in mathematics and science. She initially pursued pharmacy at Xavier University in New Orleans but later transitioned to a career in technology. This shift was influenced by her interest in mathematics and her determination to overcome racial and gender barriers in the professional world.
Career Highlights
In 1955, Annie Easley began her career at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), which became NASA in 1958. She started as a "human computer," performing complex mathematical calculations by hand. Easley quickly transitioned to programming, learning computer languages like FORTRAN and contributing to projects such as the development of software for the Centaur rocket. Her work included supporting energy projects, such as battery technology for early hybrid vehicles. Easley’s career spanned over three decades, during which she was a trailblazer for women and minorities in STEM.
Major Achievements
- Contributed to software development for the Centaur rocket, which played a crucial role in numerous space missions.
- Worked on alternative energy projects, including research on battery technology for hybrid vehicles.
- Mentored and advocated for women and minorities in STEM, helping to diversify the field.
- Participated in the development of code used in energy-conversion systems and satellite-launch vehicles.
Famous Quotes
- "If I can’t work with you, I will work around you."
- "You are never too old, and if you want to, as my mother said, you can do anything you want to, but you have to work at it."
Interesting Facts
- Easley was one of the first African-American women to work as a computer scientist at NASA.
- She earned a degree in mathematics from Cleveland State University while working full-time.
- Easley was actively involved in outreach, encouraging young people to pursue careers in STEM.
- She was among the few African-American women in her field during her tenure, breaking numerous racial and gender barriers.
- Easley continued to work at NASA for 34 years, retiring in 1989.
Legacy / Influence
Annie Easley’s contributions to NASA and her pioneering efforts in the STEM fields have left a lasting impact. She broke barriers for women and African Americans, paving the way for greater diversity in technology and engineering. Easley’s work, particularly in energy conversion and space exploration, continues to influence current technologies and inspire future generations of scientists and engineers to pursue their dreams, regardless of societal obstacles.
FAQ
Q: Why is Annie Easley famous?
A: Annie Easley is famous for her work as a computer scientist and mathematician at NASA, where she contributed to the development of software for the Centaur rocket and alternative energy projects.
Q: What was one of her key contributions to NASA?
A: One of her key contributions was developing software for the Centaur rocket, which was vital in launching satellites and space probes.
Q: How did she impact diversity in STEM fields?
A: Easley was a pioneer for women and African Americans in STEM, mentoring others and advocating for greater diversity in these fields.