Short Summary
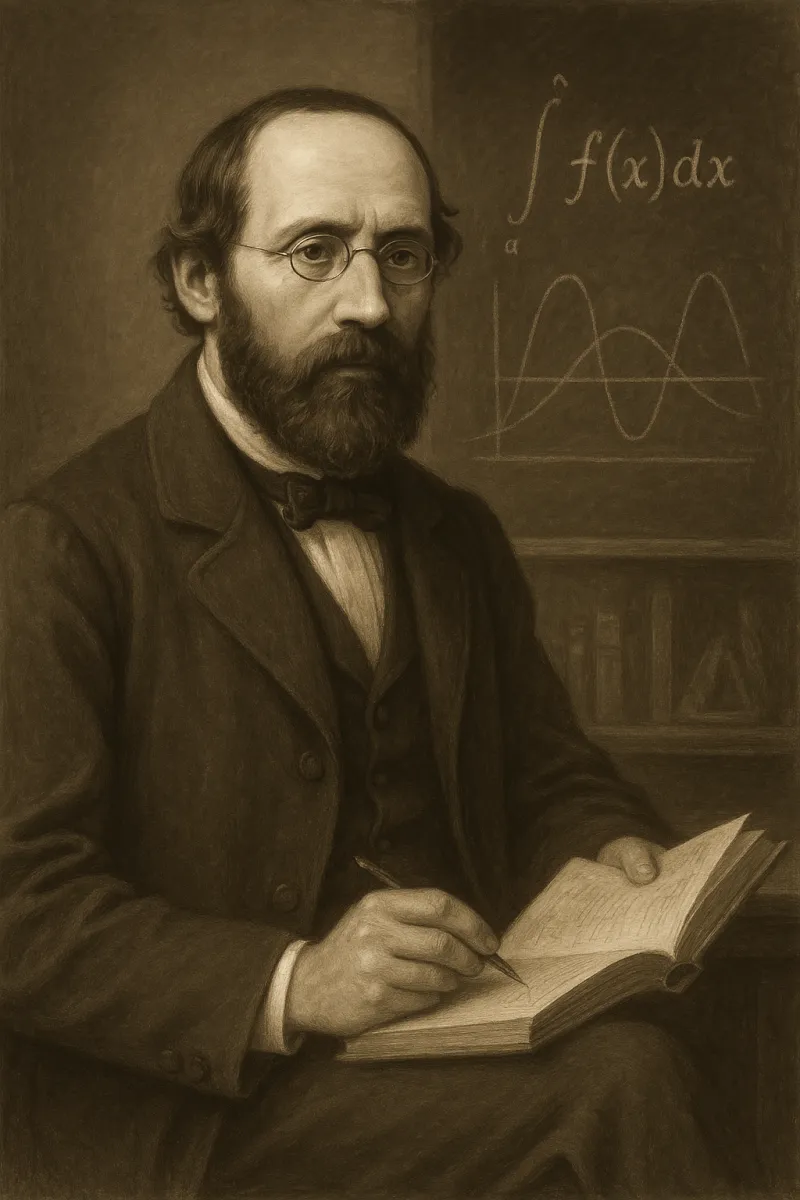
Bernhard Riemann was a pioneering German mathematician whose work laid the groundwork for several areas of mathematics and physics. He is most renowned for his contributions to differential geometry and complex analysis, which have had profound implications in the development of the theories of relativity and quantum mechanics. His Riemann Hypothesis remains one of the most famous unsolved problems in mathematics. Riemann's innovative ideas have made him a central figure in the history of mathematics.
Early Life & Education
Born on September 17, 1826, in Breselenz, Kingdom of Hanover, Bernhard Riemann was the second of six children in a Lutheran pastor's family. His early education was marked by a keen aptitude for mathematics, which was recognized by his teachers. Riemann attended the University of Göttingen in 1846, where he initially studied theology before switching to mathematics under the influence of Carl Friedrich Gauss. He later moved to the University of Berlin to study under eminent mathematicians such as Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi and Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet, which profoundly shaped his mathematical perspective.
Career Highlights
Riemann returned to the University of Göttingen, where he completed his habilitation thesis on the foundations of geometry, introducing what is now known as Riemannian geometry. In 1859, he was appointed as a full professor at Göttingen, where he continued to develop his groundbreaking ideas. During his career, Riemann delved into topics such as complex analysis, real analysis, and number theory. His work on the distribution of prime numbers and the Riemann Hypothesis significantly influenced future mathematical research, though he passed away at the early age of 39 in 1866.
Major Achievements
- Formulated the Riemann Hypothesis: An unsolved problem regarding the distribution of prime numbers.
- Developed Riemannian geometry: A framework that extended the study of geometry to higher dimensions.
- Advanced complex analysis: Through his work on Riemann surfaces, he provided insights into the behavior of complex functions.
- Contributed to real analysis: Introduced the Riemann integral, a foundational concept in calculus.
Famous Quotes
- "The method of the differential calculus extends to every question which can be expressed in terms of continuous quantity."
- "If only I had the theorems! Then I should find the proofs easily enough."
Interesting Facts
- Bernhard Riemann was a devout Christian and his faith played a significant role in his life and work.
- He was a student of the legendary mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss, who greatly influenced his thinking.
- Riemann suffered from poor health throughout his life, which limited his ability to work at times.
- His work laid the foundation for Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity.
- The Riemann Hypothesis, posed in 1859, remains one of the seven "Millennium Prize Problems" with a reward of one million dollars for a correct solution.
Legacy / Influence
Riemann's work fundamentally changed the landscape of mathematics and physics. His contributions to geometry and complex analysis have had enduring effects, influencing fields such as topology and mathematical physics. The Riemann Hypothesis continues to drive research in number theory. His ideas underpin the mathematical framework of general relativity, highlighting the lasting impact of his innovative thinking.
FAQ
Q: Why is Bernhard Riemann famous?
A: He is famous for his groundbreaking contributions to mathematics, especially in differential geometry and complex analysis, and for the Riemann Hypothesis.
Q: What is the Riemann Hypothesis?
A: It is a conjecture regarding the distribution of prime numbers, proposed by Bernhard Riemann in 1859, and remains unsolved.
Q: How did Riemann influence physics?
A: His work on Riemannian geometry provided the mathematical foundation for Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity.