Short Summary
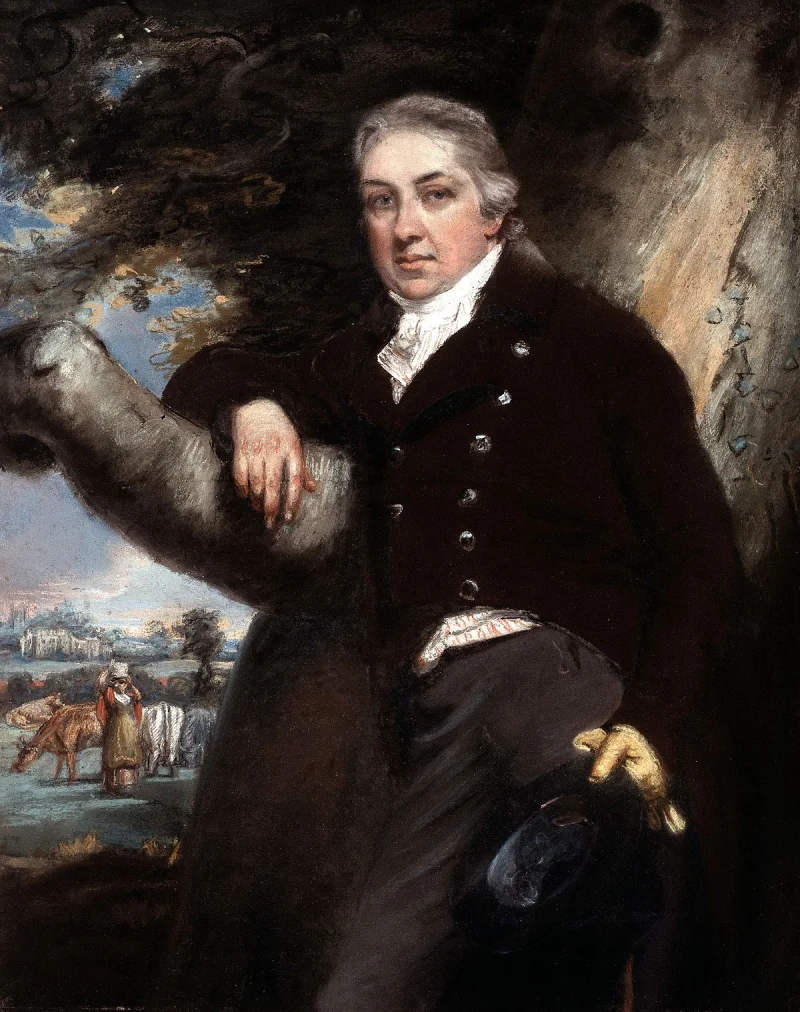
Edward Jenner was an English physician and scientist renowned for developing the smallpox vaccine, the world's first vaccine. His pioneering work in immunology laid the foundation for modern vaccination practices and has saved countless lives. Jenner is often referred to as the "father of immunology," and his contributions have had a lasting impact on public health and medicine.
Early Life & Education
Edward Jenner was born on May 17, 1749, in Berkeley, Gloucestershire, England, to a clergyman father. From a young age, he showed an interest in nature and science. He was educated at Cirencester Grammar School and later apprenticed to Daniel Ludlow, a local surgeon, at the age of 14. Jenner's medical education continued in London under the renowned surgeon John Hunter, who greatly influenced his scientific thinking and encouraged his curiosity in natural science. This early exposure to medical practice and scientific inquiry set the stage for his groundbreaking work in immunology.
Career Highlights
Edward Jenner began his medical career as a country doctor in his hometown of Berkeley. His most significant contribution came in 1796 when he conducted his famous experiment using cowpox to inoculate against smallpox, a practice that would come to be known as vaccination. Jenner published his findings in 1798, which demonstrated the effectiveness of the cowpox vaccine in providing immunity to smallpox. Although initially met with skepticism, his work gained acceptance and led to widespread adoption of vaccination. Jenner continued to promote vaccination and conducted further research until his death in 1823.
Major Achievements
- Developed the first successful smallpox vaccine, establishing the practice of vaccination.
- Published "An Inquiry into the Causes and Effects of the Variolae Vaccinae," detailing his vaccine research.
- Contributed to the eventual eradication of smallpox, declared by the World Health Organization in 1980.
- Laid the foundations for the field of immunology, influencing future vaccine development.
Famous Quotes
- "The deviation of man from the state in which he was originally placed by nature seems to have proved to him a prolific source of diseases."
- "I shall endeavor still to keep my mind in a state of easy tranquility."
Interesting Facts
- Jenner's first vaccination experiment was conducted on an eight-year-old boy named James Phipps.
- He used cowpox, a disease affecting cattle, to create immunity against smallpox.
- Jenner's work was initially met with resistance and skepticism from the medical community.
- The term "vaccine" is derived from the Latin word "vacca," meaning cow, in honor of his work with cowpox.
- Jenner was also a skilled naturalist and made significant contributions to the study of bird migration.
Legacy / Influence
Edward Jenner's pioneering work in vaccination has had a profound and lasting impact on public health. His development of the smallpox vaccine laid the groundwork for modern immunology and the subsequent development of vaccines for other infectious diseases. Jenner's legacy lives on in the continued fight against preventable diseases, and his contributions have saved millions of lives around the world, making him a pivotal figure in medical history.
FAQ
Q: Why is Edward Jenner famous?
A: He is famous for developing the first successful smallpox vaccine, which laid the foundation for modern vaccination practices.
Q: What was Edward Jenner's most significant contribution?
A: His most significant contribution was the development of the smallpox vaccine, which eventually led to the eradication of the disease.
Q: How did Edward Jenner test his smallpox vaccine?
A: He tested his vaccine by inoculating an eight-year-old boy with cowpox, which provided immunity against smallpox.