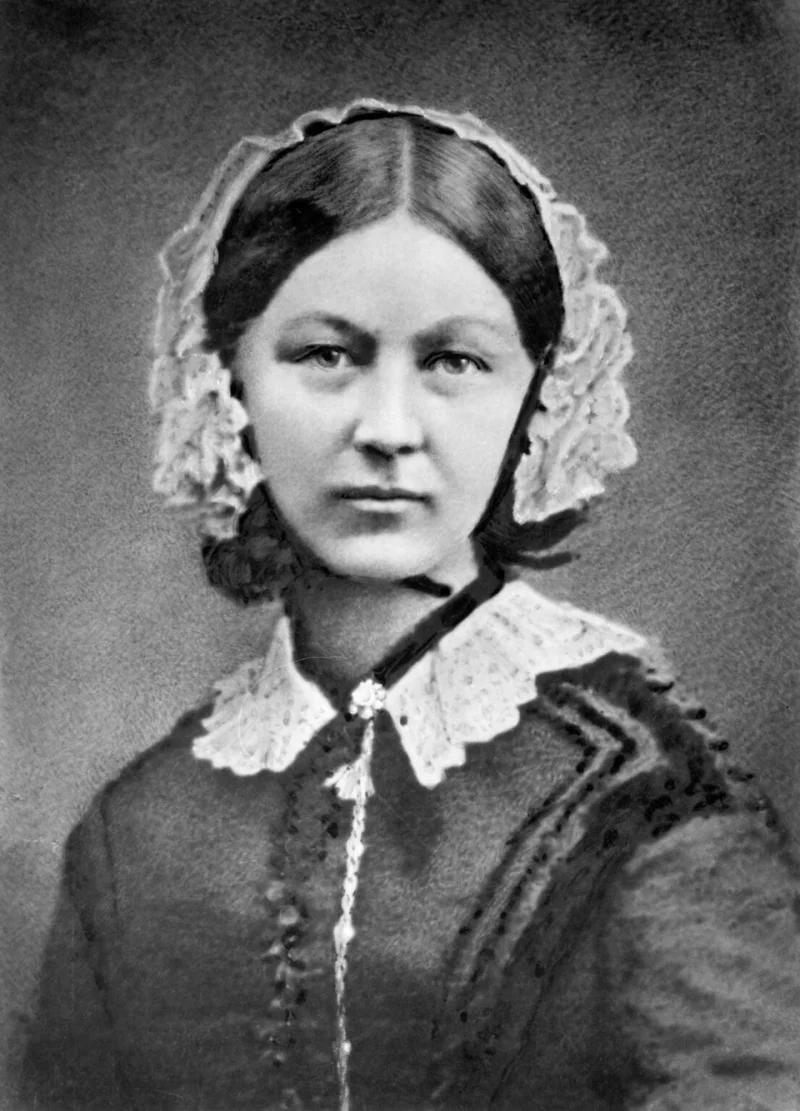Short Summary
Florence Nightingale was a pioneering figure in the field of nursing, known for her significant contributions to healthcare and patient care during the 19th century. Her most renowned achievement was her work during the Crimean War, where she improved the sanitary conditions of the military hospitals, significantly reducing the mortality rate. She is often referred to as "The Lady with the Lamp" due to her nightly rounds to tend to wounded soldiers. Her legacy lives on in modern nursing practices and healthcare reforms.
Early Life & Education
Florence Nightingale was born on May 12, 1820, in Florence, Italy, into a wealthy British family. Her parents, William and Frances Nightingale, were well-educated and encouraged her intellectual pursuits. Florence showed an early interest in mathematics and statistics, which later influenced her work in healthcare. Despite societal expectations for women of her status, she pursued her interest in nursing, which was considered an unsuitable profession for women of her class at the time. Her education included studies in languages, philosophy, and mathematics, which laid a foundation for her future contributions to healthcare.
Career Highlights
Florence Nightingale's career took a pivotal turn in 1854 when she was appointed to oversee the nursing of soldiers in the Crimean War. Her efforts in improving sanitation and organizing the care of wounded soldiers reduced the death rate significantly. After the war, she returned to England, where she continued to advocate for healthcare reform. She established the Nightingale Training School for Nurses at St. Thomas' Hospital in London, which set standards for nursing education. Her work laid the groundwork for modern nursing practices and established nursing as a respected profession.
Major Achievements
- Reformed Military Hospitals: Improved sanitary conditions and reduced mortality rates during the Crimean War.
- Established Nursing Schools: Founded the Nightingale Training School for Nurses, setting standards for nursing education.
- Influenced Healthcare Policy: Advocated for healthcare reform, influencing hospital design and sanitation.
- Pioneered Use of Statistics: Used statistical methods to advocate for health reforms.
Famous Quotes
- "I attribute my success to this—I never gave or took any excuse."
- "The very first requirement in a hospital is that it should do the sick no harm."
Interesting Facts
- Florence Nightingale was named after the city of her birth, Florence, Italy.
- She was the first woman to be awarded the Order of Merit in 1907.
- Nightingale was a pioneer in the use of infographics and statistics to present data effectively.
- She continued her work despite being mostly bedridden due to illness later in life.
- Her birthday, May 12, is celebrated as International Nurses Day.
Legacy / Influence
Florence Nightingale's influence on nursing and healthcare is profound and enduring. She established nursing as a respected profession and introduced practices that significantly improved patient care and hospital administration. Her emphasis on hygiene and sanitation has had a lasting impact on public health policies worldwide. Her work has inspired generations of nurses and healthcare professionals, and her legacy continues to be celebrated and built upon in modern healthcare systems.
FAQ
Q: Why is Florence Nightingale famous?
A: She is famous for her pioneering work in nursing and healthcare reform, particularly during the Crimean War.
Q: What is Florence Nightingale's nickname?
A: She is known as "The Lady with the Lamp" for her nightly rounds tending to soldiers.
Q: What did Florence Nightingale contribute to healthcare?
A: She contributed to improved sanitary conditions, established nursing education, and influenced healthcare policies.