Short Summary
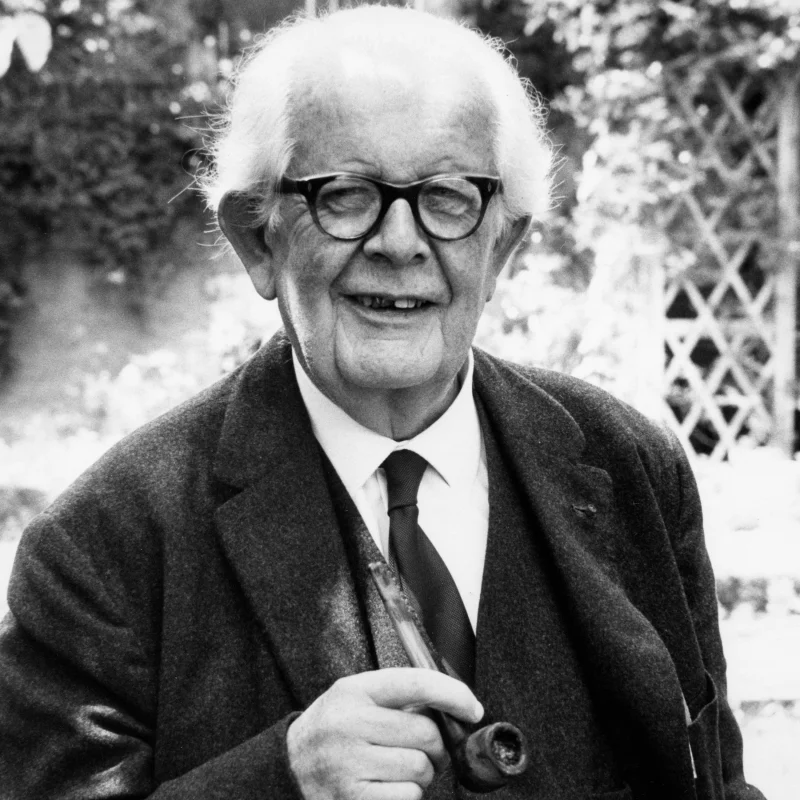
Jean Piaget was a Swiss psychologist renowned for his pioneering work in child development. His theory of cognitive development has profoundly influenced our understanding of how children learn and think. Piaget is famous for introducing the idea that children pass through distinct stages of cognitive growth, challenging previous notions of childhood intelligence. His work has had a lasting impact on education and psychology, making him a key figure in developmental psychology.
Early Life & Education
Jean Piaget was born on August 9, 1896, in Neuchâtel, Switzerland. He was the eldest son of Arthur Piaget, a professor of medieval literature, and Rebecca Jackson. From a young age, Piaget displayed a keen interest in nature and science, writing his first scientific paper on the albino sparrow at the age of 11. He attended the University of Neuchâtel, where he studied zoology and obtained his Ph.D. in 1918. His early exposure to philosophical and biological concepts laid the foundation for his future work in psychology.
Career Highlights
Jean Piaget's career spanned several decades, during which he made significant contributions to psychology and education. After completing his doctoral studies, he worked at the Alfred Binet Laboratory in Paris, where he began observing children's intellectual development. In 1921, he was appointed as the Director of the International Bureau of Education. Piaget's major career milestone was the development of his theory of cognitive development, which he elaborated through extensive research and publications. His work led to the establishment of the International Center for Genetic Epistemology in Geneva in 1955, further cementing his influence in the field.
Major Achievements
- Developed the theory of cognitive development, outlining stages that explain how children's thinking evolves.
- Published over 50 books and hundreds of articles, contributing extensively to the field of psychology.
- Founded the International Center for Genetic Epistemology, fostering research in cognitive development.
- Received numerous honorary degrees and awards for his contributions to psychology and education.
Famous Quotes
- "The goal of education is not to increase the amount of knowledge but to create the possibilities for a child to invent and discover."
- "Intelligence is what you use when you don’t know what to do."
Interesting Facts
- Piaget initially studied mollusks, publishing several papers on the subject before turning to psychology.
- His theory of cognitive development was considered revolutionary and challenged existing theories of child intelligence.
- Piaget's research was based on detailed observations of his own children.
Legacy / Influence
Jean Piaget's work has had a profound impact on both psychology and education. His theory of cognitive development revolutionized our understanding of child learning processes and has influenced educational practices worldwide. Piaget's emphasis on stages of development has also shaped curricula and teaching strategies, encouraging educators to tailor instruction to developmental stages. His contributions continue to inspire research and debate in developmental psychology.
FAQ
Q: Why is Jean Piaget famous?
A: He is famous for his theory of cognitive development in children, which revolutionized the understanding of child psychology and education.
Q: What are the stages of Piaget's cognitive development theory?
A: The stages include the sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, and formal operational stages.
Q: How did Piaget conduct his research?
A: He conducted detailed observations and experiments with children, including his own, to develop his theories.