Short Summary
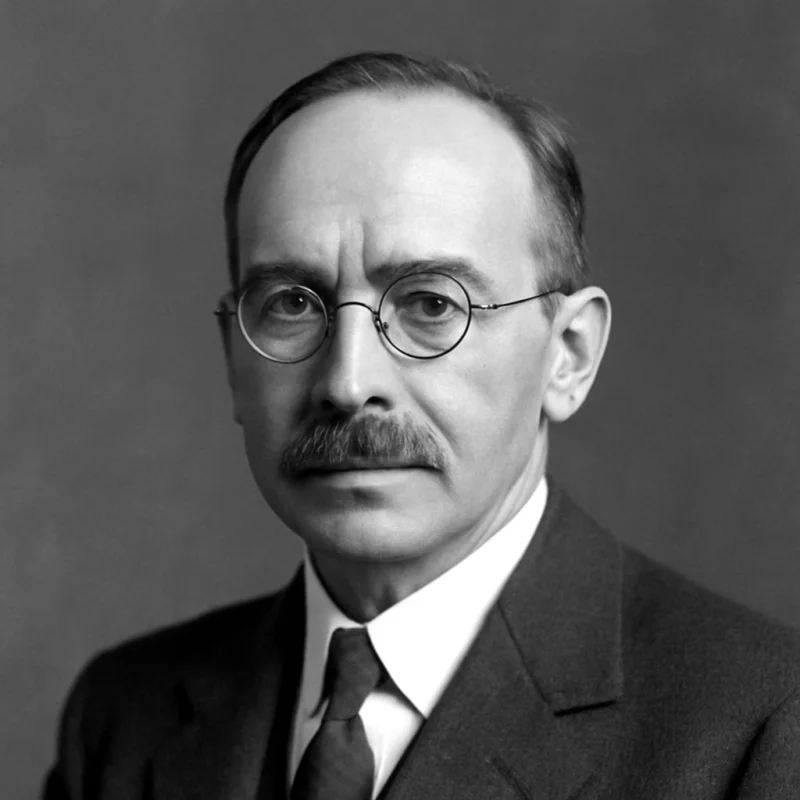
Niels Bohr was a pioneering Danish physicist renowned for his foundational contributions to understanding atomic structure and quantum theory. He is most famous for developing the Bohr model of the atom, which introduced the theory of electrons orbiting the nucleus in quantized energy levels. Bohr's work set the stage for modern quantum mechanics and earned him the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1922. His influence extended beyond physics as he played a crucial role in scientific developments during the 20th century.
Early Life & Education
Niels Bohr was born on October 7, 1885, in Copenhagen, Denmark, into an intellectually stimulating environment. His father, Christian Bohr, was a professor of physiology, and his mother, Ellen, came from a prominent banking family. Bohr showed a keen interest in science and mathematics from a young age. He pursued his education at the University of Copenhagen, where he studied under the tutelage of Christian Christiansen, earning his master's degree in 1909 and his doctorate in 1911. His early academic influences laid the groundwork for his future groundbreaking research in theoretical physics.
Career Highlights
After completing his doctorate, Bohr moved to England to work with J.J. Thomson at the Cavendish Laboratory and later with Ernest Rutherford at the University of Manchester. It was during his time with Rutherford that Bohr developed his revolutionary atomic model in 1913, incorporating quantum theory to explain the stability of atoms. In 1920, he founded the Institute of Theoretical Physics at the University of Copenhagen, which became a leading center for research in quantum mechanics. His collaboration with many prominent physicists of the time, including Werner Heisenberg and Max Planck, further solidified his influential role in the scientific community.
Major Achievements
- Developed the Bohr Model of the Atom: Introduced the quantized shell model to explain the structure and behavior of atoms.
- Nobel Prize in Physics (1922): Awarded for his services in the investigation of the structure of atoms and the radiation emanating from them.
- Contributions to Quantum Mechanics: Played a significant role in the development of quantum theory and its interpretation.
- Manhattan Project: Contributed to the Allied effort in World War II by working on the development of nuclear weapons.
Famous Quotes
- "An expert is a person who has made all the mistakes that can be made in a very narrow field."
- "Anyone who is not shocked by quantum theory has not understood it."
Interesting Facts
- Bohr's institute in Copenhagen became a hub for physicists fleeing Nazi Germany.
- He was an avid football player and fan, even winning a prize in a competition held by the Danish Academy of Sciences.
- Bohr was knighted by the Danish government in 1947.
Legacy / Influence
Niels Bohr's work on atomic structure and quantum theory fundamentally transformed the field of physics. His theories laid the groundwork for future research and developments in quantum mechanics, influencing generations of physicists. The Bohr model remains a pivotal step in the evolution of atomic theory, and his legacy continues through the scientists he mentored and the ongoing research at the institute he founded.
FAQ
Q: Why is Niels Bohr famous?
A: He is famous for developing the Bohr model of the atom and his contributions to quantum mechanics.
Q: Did Niels Bohr win a Nobel Prize?
A: Yes, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1922.
Q: What was Niels Bohr's contribution to the Manhattan Project?
A: He contributed by advising on nuclear fission and reactor design during World War II.
Q: What is the Bohr model of the atom?
A: It is a model that describes electrons orbiting the nucleus at fixed energy levels.