Short Summary
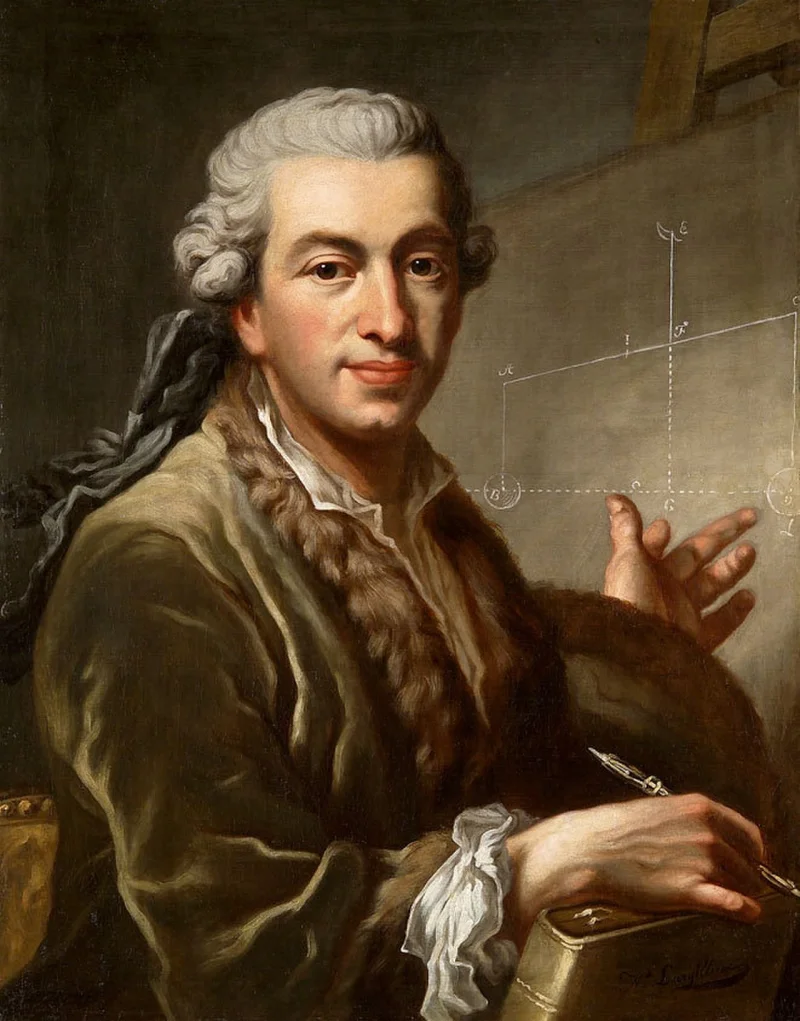
Pierre-Simon Laplace was a prominent French mathematician and astronomer whose work significantly advanced the fields of mathematics, statistics, physics, and astronomy. He is most famous for his development of Laplace's equation and the Laplace transform, foundational tools in differential equations and engineering. His comprehensive five-volume work, "Mécanique Céleste," translated Newton’s gravitational studies into mathematical language that could predict planetary motion. Laplace's contributions have had a lasting impact, establishing him as a pivotal figure in the scientific revolution of the 18th and 19th centuries.
Early Life & Education
Born on March 23, 1749, in Beaumont-en-Auge, Normandy, Pierre-Simon Laplace was the son of a cider merchant. His early education was at a local school, where he displayed exceptional mathematical talent. Recognizing his potential, his family arranged for him to study in Caen at the University of Caen Normandy. There, he was profoundly influenced by mathematicians such as Pierre Le Canu. Despite his humble beginnings, Laplace's academic prowess facilitated his move to Paris, where he would eventually become a professor of mathematics at the École Militaire.
Career Highlights
Laplace's career was marked by his appointment as a professor at the École Militaire in Paris, where he taught Napoleon Bonaparte. His work in astronomy, particularly the stability of the solar system, set the foundation for celestial mechanics. Laplace also held various political roles, including Minister of the Interior during Napoleon's regime, though his tenure was brief. His career was characterized by his ability to apply mathematical principles to solve complex physical problems, cementing his reputation as a leading scientist of his time.
Major Achievements
- Developed the Laplace Equation: A cornerstone in the theory of partial differential equations.
- Authored "Mécanique Céleste": Translated Newtonian physics into comprehensive mathematical form.
- Introduced the Laplace Transform: A mathematical transformation integral to engineering and physics.
- Explored the Stability of the Solar System: Proved that planetary orbits remain stable over long periods.
Famous Quotes
- "What we know is not much. What we do not know is immense."
- "The weight of evidence for an extraordinary claim must be proportioned to its strangeness."
Interesting Facts
- Laplace worked closely with Napoleon, yet fell out of favor when political tides shifted.
- He was made a marquis by King Louis XVIII after the fall of Napoleon.
- His work laid the groundwork for the development of statistical mechanics.
Legacy / Influence
Laplace's influence extends across several scientific disciplines. His mathematical formulations form the backbone of many modern engineering and physics applications. The Laplace Transform and Laplace's Equation are fundamental in the study of systems dynamics and electromagnetism. His work in celestial mechanics paved the way for future astronomers, and his philosophical approach to probability influenced the development of statistical inference.
FAQ
Q: Why is Pierre-Simon Laplace famous?
A: He is renowned for his contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and physics, particularly for Laplace's equation and his work in celestial mechanics.
Q: What was Laplace's role in astronomy?
A: He translated Newtonian gravitational principles into a mathematical framework, predicting planetary motion.
Q: Did Laplace have any involvement in politics?
A: Yes, he briefly served as Minister of the Interior under Napoleon.