Short Summary
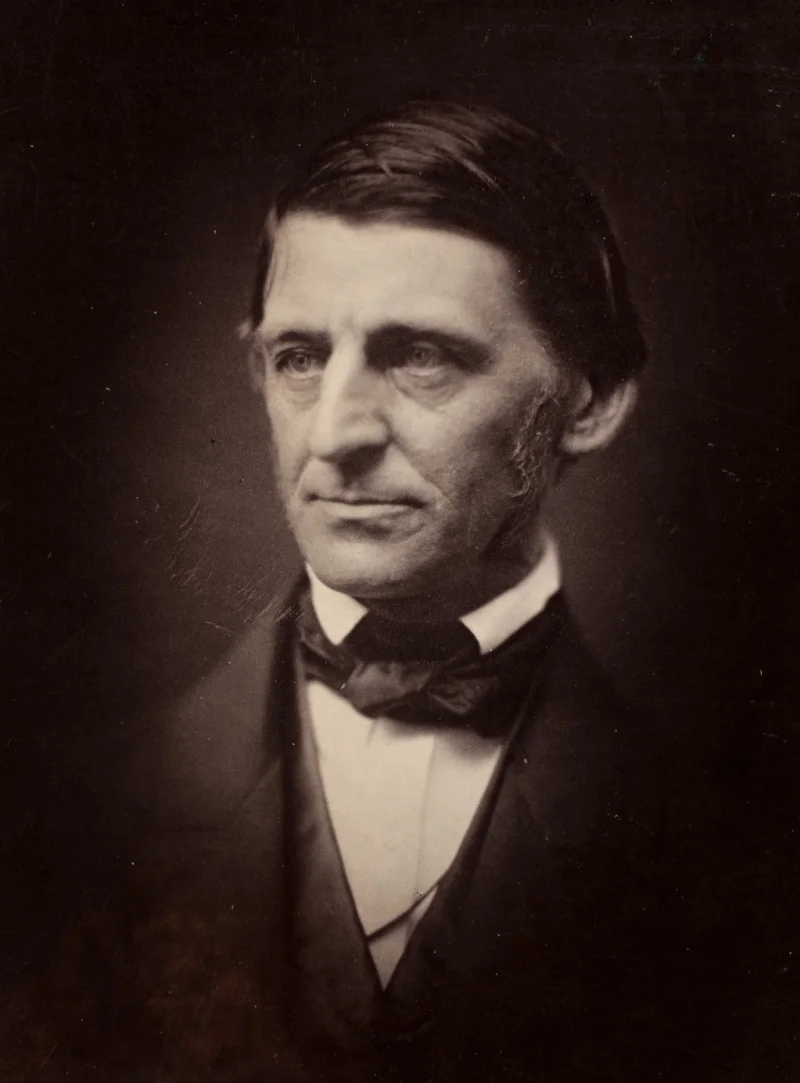
Ralph Waldo Emerson was a renowned American essayist, lecturer, philosopher, and poet who led the transcendentalist movement of the mid-19th century. He is best known for his essays, such as "Self-Reliance" and "Nature," which emphasized individualism and the inherent goodness of people and nature. Emerson's works and ideas significantly influenced American thought and literature, earning him a prominent place in philosophical and literary history.
Early Life & Education
Ralph Waldo Emerson was born on May 25, 1803, in Boston, Massachusetts, to a family with a strong religious background. His father, William Emerson, was a Unitarian minister, but he died when Emerson was just eight years old. Emerson was raised by his mother, Ruth Haskins, and his aunt, Mary Moody Emerson, who played a significant role in his upbringing. He attended the Boston Latin School and later enrolled at Harvard College at the age of 14, graduating in 1821. Emerson briefly taught school before attending Harvard Divinity School, where he prepared for the Unitarian ministry.
Career Highlights
Emerson began his career as a Unitarian minister, but he soon resigned from the clergy due to his growing philosophical differences with church doctrine. He embarked on a lecture tour, which became a significant platform for his ideas. In 1836, he published "Nature," a seminal work that laid the foundation for transcendentalism. Emerson became a central figure in the transcendentalist movement, associating with other prominent intellectuals like Henry David Thoreau. His "Essays: First Series" and "Essays: Second Series" further established his reputation as a leading thinker, addressing themes of individuality, freedom, and the connection between humans and nature.
Major Achievements
- Published "Nature" in 1836, which became a cornerstone of transcendentalism.
- Delivered his famous "The American Scholar" address in 1837, calling for cultural independence.
- Authored influential essays like "Self-Reliance" and "The Over-Soul" that emphasized individualism and self-trust.
- Mentored and influenced other American writers, including Henry David Thoreau and Walt Whitman.
Famous Quotes
- "To be yourself in a world that is constantly trying to make you something else is the greatest accomplishment."
- "What lies behind us and what lies before us are tiny matters compared to what lies within us."
Interesting Facts
- Emerson's father passed away when he was just eight years old, impacting his family life significantly.
- He was a staunch advocate for abolition and supported the abolitionist movement.
- His 1837 address "The American Scholar" was described by Oliver Wendell Holmes as America's "Intellectual Declaration of Independence."
- Emerson was a key figure in establishing the Transcendental Club, which included members like Margaret Fuller and Alcott.
Legacy / Influence
Emerson's influence extends far beyond his own time, as his writings and ideas continue to inspire and shape American thought and literature. His emphasis on individualism and self-reliance has permeated American culture, fostering a spirit of personal independence. His works laid the groundwork for subsequent American writers and philosophers, securing his place as a pivotal figure in the development of American intellectual history.
FAQ
Q: Why is Ralph Waldo Emerson famous?
A: He is famous for his role in leading the transcendentalist movement and for his influential essays on individuality and self-reliance.
Q: What is transcendentalism?
A: Transcendentalism is a philosophical movement that emphasizes the inherent goodness of people and nature, advocating for self-reliance and individual intuition.
Q: What are some of Emerson's most famous works?
A: Some of his most famous works include "Nature," "Self-Reliance," and "The American Scholar."
Q: How did Emerson influence other writers?
A: Emerson mentored writers like Henry David Thoreau and influenced others like Walt Whitman, shaping their literary and philosophical perspectives.