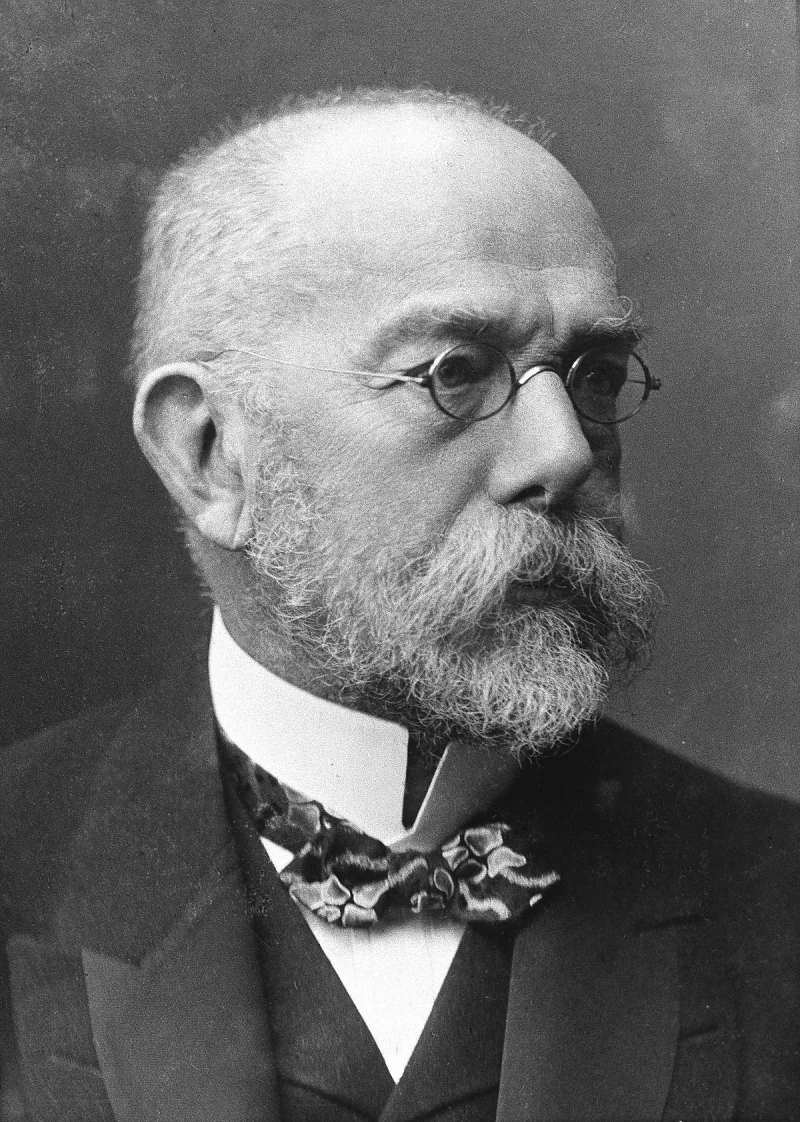Short Summary
Alexander Fleming was a Scottish bacteriologist best known for discovering penicillin, the first true antibiotic, which revolutionized medicine and saved countless lives. Born in 1881, his groundbreaking work in microbiology led to the development of treatments for bacterial infections that were once considered fatal. Fleming's discovery marked a turning point in medical history, earning him the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1945, shared with Howard Florey and Ernst Boris Chain.
Early Life & Education
Born on August 6, 1881, in Lochfield, Scotland, Fleming was the seventh of eight children in a farming family. After his father’s death, the family moved to London, where he attended the Royal Polytechnic Institution. He worked briefly as a shipping clerk before enrolling in St. Mary's Hospital Medical School in 1901, thanks to a scholarship. His education was interrupted by service in the Territorial Army, but he later returned to complete his studies. Influenced by his brother Tom, a physician, and his mentor Sir Almroth Wright, he developed a keen interest in bacteriology.
Career Highlights
Fleming began his career at St. Mary's Hospital, where he conducted research on bacterial infections. During World War I, he served as a captain in the Royal Army Medical Corps, observing the ineffectiveness of antiseptics in treating infected wounds, which fueled his research. In 1928, he discovered penicillin accidentally while researching staphylococci bacteria. Fleming noted that a mold contamination had killed the surrounding bacteria, leading to his revolutionary discovery. Despite initial challenges in mass production, his work laid the foundation for antibiotic development, altering the course of medical treatment.
Major Achievements
- Discovered penicillin in 1928, which became the first widely used antibiotic.
- Published numerous research papers on bacteriology and immunology.
- Awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1945.
- Received numerous honorary degrees from universities worldwide.
Famous Quotes
- "One sometimes finds what one is not looking for."
- "It is the lone worker who makes the first advance in a subject; the details may be worked out by a team."
Interesting Facts
- Fleming was an accomplished artist and often drew caricatures of his colleagues.
- He named the substance he discovered "penicillin" after the Penicillium mold that produced it.
- Despite his monumental discovery, Fleming remained modest and often credited others for the development of penicillin.
- He was knighted in 1944 for his contributions to medicine.
Legacy / Influence
Fleming's discovery of penicillin transformed the field of medicine by introducing antibiotics as a standard treatment for bacterial infections. This breakthrough led to the development of other antibiotics and revolutionized healthcare, significantly reducing mortality rates from infectious diseases. His work continues to influence medical research, and antibiotics remain a crucial component in modern medicine.
FAQ
Q: Why is Alexander Fleming famous?
A: He is famous for discovering penicillin, the first true antibiotic, which revolutionized medicine.
Q: What was Fleming's primary field of study?
A: His primary field of study was bacteriology and immunology.
Q: Did Fleming work alone on penicillin?
A: While Fleming discovered penicillin, further development was carried out by scientists like Howard Florey and Ernst Boris Chain.
Q: How did Fleming's discovery impact medicine?
A: It introduced antibiotics, significantly reducing deaths from bacterial infections and changing treatment approaches.